Understanding the GPM¶
A Gaussian Process (GP) model uses a Bayesian regression approach. This method models the data by considering an infinite function space. It gives a probability to every function within this infinite space, corresponding to how likely the function is to model the data. Since representing an infinite function space is computationally intractable, we use Gaussian Processes to represent the distribution of functions over an infinite domain. We utilized 3 GPs in our model, each with a covariance function chosen to cover specific behavior we wanted from our model. The chosen covariance kernels are listed below: 1. Exponentiated Quadratic Kernel for long-term steady growth. 2. Rational Kernel for short to medium length fluctuations. 3. Periodic Kernel for medium length periodic behavior. 4. White Noise and Matern32 kernels as noise modelers.
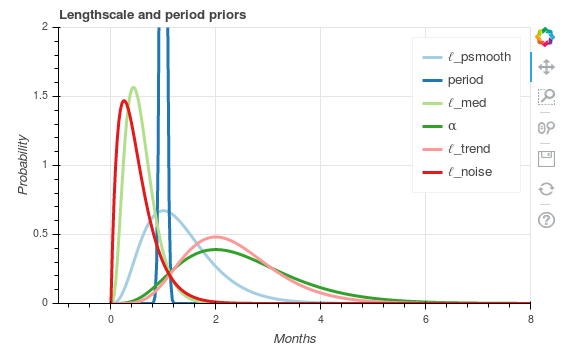
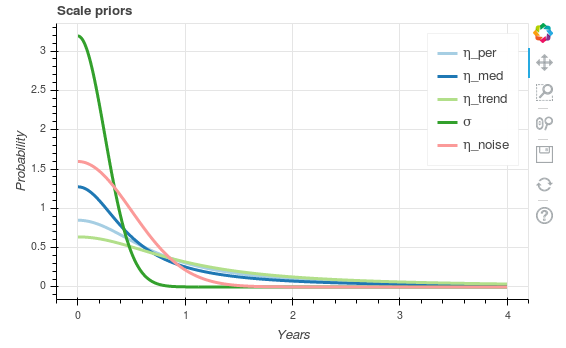
Each of these kernels can be described in further detail by hyper-parameter distributions. The plots of these distributions are shown below: